Physical Therapy
Botox® Injections for Neurological Conditions:
Botox injections are quite successfully given for neurological conditions such as cervical dystonia, blepharospasm, spasmodic torticollis, spasticity, hemifacial spasms, and hand dystonia. Injections are sometimes given for the treatment of migraine headaches. Our Neurologists are certified to give Botox injections for neurological conditions in the comfort of our office. Please call 815.226.1906 to schedule an appointment to discuss this option with one of our physicians.
Please contact our office at 815-226-1906 to schedule an appointment to discuss Botox® Injections for Neurological Conditions with one of our Neurologists
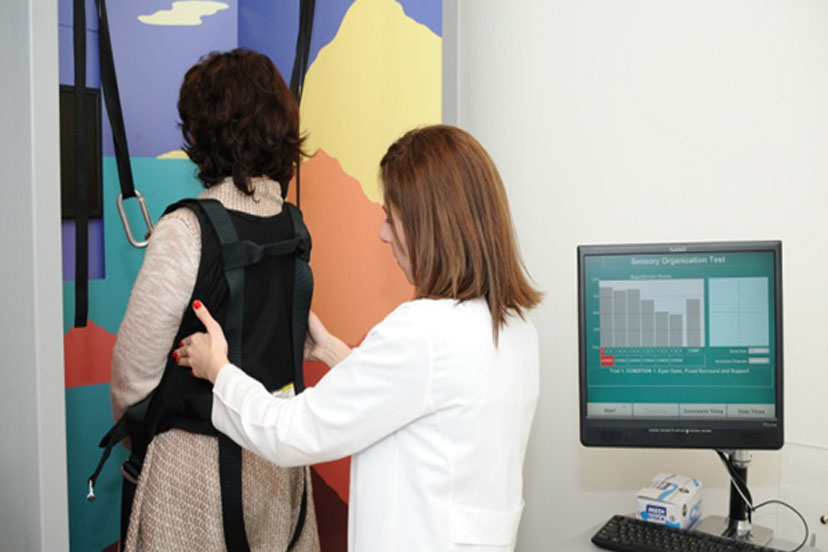

Computerized Dynamic Posturography:
Computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) is an established test of postural stability. While ENG and rotation testing assess visual-vestibular interactions, CDP provides information about motor control or balance function under varying environmental conditions.
The ability to maintain balance depends not only on vision and the vestibular system, but also on information that the brain receives from the muscles and joints which provide clues such as the direction of head turn and the texture and slope of the walking surface. CDP tests the relationships among all balance system components--eyes, somatosensory system, and vestibular system. It measures the person's response to environments in which the amount of reliable information from the eyes and somatosensory system is varied.
The test involves standing on a platform, typically with some form of visual target to watch. The platform and/or the visual target move while pressure gauges under the platform record shifts in body weight (body sway) as the person being tested maintains balance. (A safety harness is worn to prevent falling during the test.) Posturography gives information about how well balance is maintained during challenging situations. It can help doctors plan other vestibular testing, as well as assist in treatment design.
Please contact our office at 815-713-9910 to schedule an appointment to discuss Computerized Dynamic Posturography with one of our Neurologists
Comprehensive Balance and Fall Prevention Clinic:
Chronic balance disorders impact a significant percentage of the population, but are very treatable with the proper therapies. Clinical research has shown that a broad spectrum of patients can benefit from comprehensive balance services, including patients who experience the following:
- Neurologic Disorders:
- Stroke
- Head Injury
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Parkinson's Disease
- Geriatrics (age-related disorders and fall prevention)
- Orthopedics:
- Joint injury and replacement
- Amputation
- Sports Medicine (sports injuries and sports conditioning)
- Vestibular disorders (dizziness / vertigo / ringing in ears)
Please contact our office at 815-713-9910 to schedule an appointment to discuss Comprehensive Balance and Fall Prevention Clinic with one of our Neurologists

Electromyography (EMG) :
Electromyography is a test that measures muscle response to stimulation. The measurement generated provides information to your Neurologist about the ability of the muscle to respond appropriately to nerve stimulation. Some conditions which may generate abnormal readings include neuropathies, cervical disorders, sciatic nerve dysfunction, and a variety of nerve syndromes, including Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Testing takes on average 20-40 minutes, and test results are available within 24 hours.
Please contact our office at 815-713-9910 to schedule an appointment to discuss In-Office EMG's with one of our Neurologists
Electroencephalography (EEG):
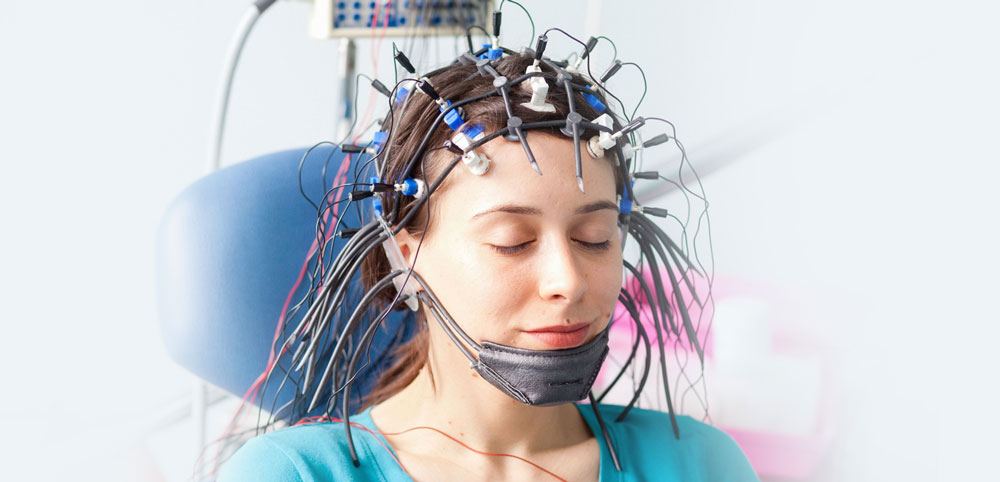
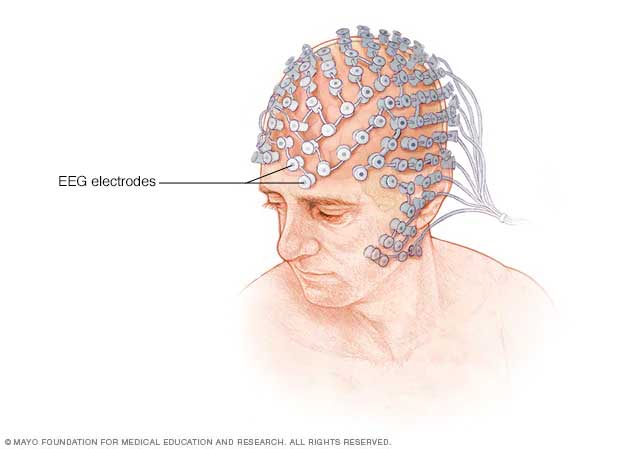
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that detects electrical activity in your brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to your scalp. Your brain cells communicate via electrical impulses and are active all the time, even when you're asleep. This activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording
An EEG is one of the main diagnostic tests for epilepsy. An EEG can also play a role in diagnosing other brain disorders.
Why it's done
An EEG can determine changes in brain activity that might be useful in diagnosing brain disorders, especially epilepsy or another seizure disorder. An EEG might also be helpful for diagnosing or treating the following disorders:
- Brain tumor
- Brain damage from head injury
- Brain dysfunction that can have a variety of causes (encephalopathy)
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
- Stroke
- Sleep disorders
An EEG might also be used to confirm brain death in someone in a persistent coma. A continuous EEG is used to help find the right level of anesthesia for someone in a medically induced coma.
Risks
EEGs are safe and painless. Sometimes seizures are intentionally triggered in people with epilepsy during the test, but appropriate medical care is provided if needed.
How you prepare
Food and medications
- Avoid anything with caffeine on the day of the test because it can affect the test results.
- Take your usual medications unless instructed otherwise.
Other precautions
- Wash your hair the night before or the day of the test, but don't use conditioners, hair creams, sprays or styling gels. Hair products can make it harder for the sticky patches that hold the electrodes to adhere to your scalp.
- If you're supposed to sleep during your EEG test, your doctor might ask you to sleep less or avoid sleep the night before your test.
- A technician measures your head and marks your scalp with a special pencil to indicate where to attach the electrodes. Those spots on your scalp might be scrubbed with a gritty cream to improve the quality of the recording.
- A technician attaches discs (electrodes) to your scalp using a special adhesive. Sometimes, an elastic cap fitted with electrodes is used instead. The electrodes are connected with wires to an instrument that amplifies the brain waves and records them on computer equipment.
Once the electrodes are in place, an EEG typically takes up to 60 minutes. Testing for certain conditions require you to sleep during the test. In that case, the test can be longer. - You relax in a comfortable position with your eyes closed during the test. At various times, the technician might ask you to open and close your eyes, perform a few simple calculations, read a paragraph, look at a picture, breathe deeply for a few minutes, or look at a flashing light.
- Video is routinely recorded during the EEG. Your body motions are captured by a video camera while the EEG records your brain waves. This combined recording can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition.
Please contact our office at 815-226-1906 to schedule an appointment to discuss Infusion Center with one of our Neurologists
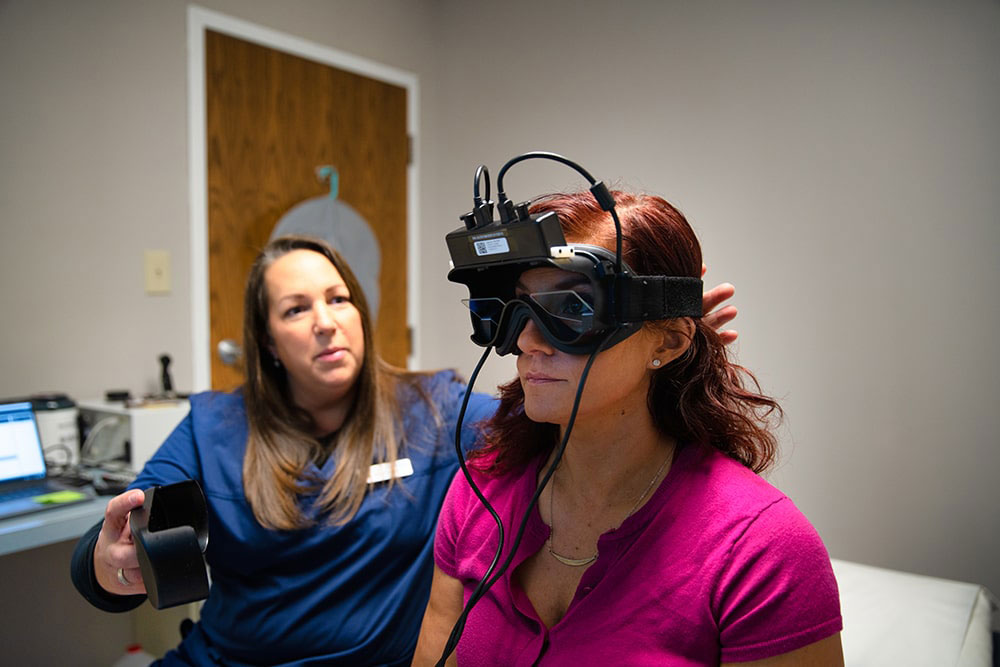
Videonystagmography (VNG):
Videonystagmography (VNG) is a test of your balance system. An extensive evaluation is required at times to determine the cause of dizziness or unsteadiness. The VNG test is the electronic recording of nystagmus (eye jerks). There are neural connections that stretch from the balance mechanism in the inner ear to the muscles of the eye. A disorder of the balance mechanism results in small eye jerks that can only be detected by a sophisticated computer. A pair of goggles, outfitted with a camera over one eye, is used to record these eye jerks during a series of tasks. The balance mechanism is monitored during tasks that consist of looking back and forth between designated points, lying in different positions, and sitting up and lying down quickly. The final portion of the test requires putting cool and warm air in the ear canal for almost a minute in order to determine if the balance mechanism of each ear can increase and decrease normally in response to stimulation. Some individuals become dizzy for 2-3 minutes, but most are able to drive home after the test without difficulty.
VNG TEST INSTRUCTIONS:
- Please dress comfortably
- The test will take about 1 hour
- Certain substances can influence the body’s response to this test giving a useless or even false result. Continue to take heart, high blood pressure and anticonvulsant medications. Questions regarding other medications should be discussed with your doctor.
- Do not drink coffee, tea, cola or any other beverage containing caffeine or alcohol within 24 hours of the test.
- Do not eat or smoke for 3 hours before the test.
- The following medications must not be taken for at least 3 days (72 hours) before the test. Aspirin, Quinine, Anti-Nausea medicine (Dramamine, Compazine, Bonine, Marezine, Phernergan, Thorazine, etc.), Anti-Vertigo medicine (Antivert, Meclizine, etc.), Tranquilizers: (Valium, Librium, Atarax, Vistaril, Equanil, Miltown, Triavil, Serax, Etrafon, etc.), Sedatives (Nembutal, Seconal, Dalmane, Doriden, Placidyl, Quaalude, Butisol, or any other sleeping pills), Narcotics and Barbiturates(Phenobarbital, Codeine, Demerol, Benadryl, Actified, Teldrin, Triaminic, any other over-the-counter cold remedies, etc.), Antihistamines (Chlortrimeton, Dimetane, Disophrol, Benadryl, Actified, any over-the-counter cold remedies, etc.) and Alcohol in any quantity (Including beer, wine and cough medicines containing alcohol.)
- PLEASE BRING SOMEBODY TO DRIVE IN CASE YOU DEVELOP DIZZINESS OR GET SICK.
Please contact our office at 815-713-9910 to schedule an appointment to discuss Videonystagmography (VNG) with one of our Neurologists
Neurological Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy for dizziness imbalance , weakness due to stroke, Parkinson's disease, Multiple sclerosis, Nerve and Muscle issues and others.
Please contact our office at 815-226-1906 to schedule an appointment to discuss Neurological Physical Therapy with one of our Neurologists
